Prostate Cancer
Urologic diseases - Symptoms - Diagnosis - Treatment
Description
Prostate cancer ( Ca.P ) is the most common malignancy in older men and the second leading cause of death from cancer in men of this age . Current data shows that every 2minutes a new case of prostate cancer ( Ca.P ) is diagnosed and every 15min. ( Minutes ) a man dies from Ca.P. 10 % of men over the age of 50 will be diagnosed with Ca.P and 3% of these will die from this disease. The number of cases is increasing for two main reasons: 1st . The average survival is significantly increasing ( i.e. people now live longer ) , and thus the disease is diagnosed more often because it affects primanly elderly people. 2nd . Diagnostic tools have evolved as we nowadays use the fraction of PSA ( prostate specific antigen ) as well as Transrectal ultrasound and prostatic biopsies, thus achieving earlier detection and treatment of this disease .
The digital rectal examination of the prostate remains the “golden standard” for immediate assessment of a swollen prostate and sometimes suffices alone this test to make the diagnosis of Ca.P.
What are the symptoms of Ca.P ?
It must be said that the symptoms of Ca.P are absent or very mild in the initial stages of the disease (frequency, nocturia, urge). We observe that these symptoms are the same as in benign prostatic hypertrophy, which is why it is so important a urological assessment to clarify the cause . In more advanced stages, there could be blood in the urine or semen and possible pains in the bones and in the back.
How will the diagnosis of Ca.P be made ?
The urologist will examine the prostate by digital rectal examination and send blood to the microbiologist to check the value of prostatic specific antigen (PSA). If one of the two is abnormal and raises suspicion of Ca.P, the only way to confirm the suspicion of Ca.P will be a biopsy of the prostate. Other conditions that can increase PSA are:- Benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH ) associated with incomplete bladder emptying
- Inflammation ( prostatitis )
- Catheterization of the bladder, etc.
The Role of PSA in the early diagnosis:
The prostate specific antigen (PSA), which received its first publicity in 1979 (from Wang et al ) is a special protein that is exclusively within the prostate cells and released into the circulation and is detected in the blood when some pathological alteration occurs in the prostate (inflammation, prostatic malignancy etc ) .
It could also be that althougt the patient has a normal PSA but an abnormal digital rectal examination (DRE), the urologist will still proceed to do prostatic biopsies.
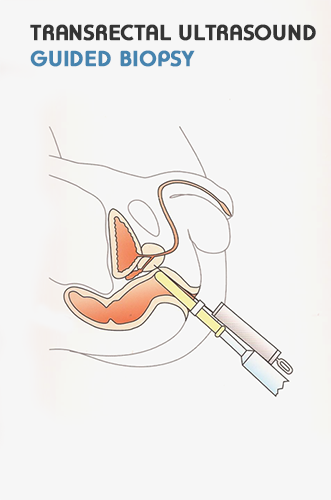
Prostate Biopsy
The biopsy of the prostate, as we said is the only valid method to determine the presence or absence of prostate cancer . The evolution of ultrasound over the past two decades have enabled detailed ultrasound imaging of the interior of the prostate, using a transducer that passes into the rectum and can provide us with remarkably clear images of prostate gland and thus “pin-point” suspicious areas that may have been missed in digital rectal examination.So with the help of a special needle attached on the head of the ultrasound , the urologist can take pieces of tissue from suspicious areas and have them examined under a microscope to tell for sure if the prostate is affected by cancer. Today we know that early diagnosis of Ca.P remarkably increases possibilities for effective treatment and cure of the disease.
More on prostate biopsy can be read here
What is the treatment of the Cancer of prostate ?
Α: Localized ( early ) disease, Ca.PTreatment options include:
- Radical prostatectomy , which means complete removal of the prostate and surrounding tissues (seminal vesicles and fat sourounding the prostate), a procedure with very good outcome.
- External radiation
- Brachytherapy (especially for smaller glands that don’t exceed the size of 40gr)
- Hormone therapy in the form of intramuscular injections.
It is important to realize that men with family history of early cancer of prostate(their fathers or brothers diagnosed with Ca P at an age younger than 55 yrs of age),should start from the age of 40 years to do regular check-ups with regular inspection of PSA, so that the detection of the disease can be done early.




