URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS
UROLOGIC DISEASES - SYMPTOMS - DIAGNOSIS - TREATMENT
Description
Urinary tract infections occur with transmission and multiplication of germs in the urinary tract. Urinary tract infections are a major part of urological workload even in the emergency cases seen in the hospital setting. Urinary tract infections in the male occur less often than in the female patients and this is due to the anatomical peculiarities of the genitourinary system in each sex. The possibility of inflammation of the urinary tract in men aged 15-55 years is small, while in men >55 years the occurrence of urinary tract infection is far more frequent.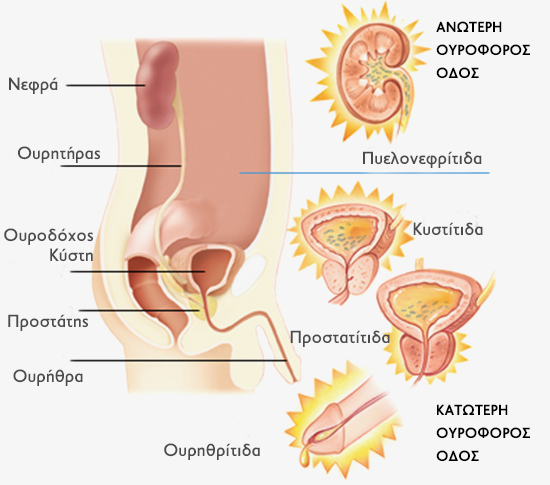
Prostatitis
It is the most common urological entity in men younger than 50 years and the third more often in men over the age of 50 , after benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer . Prostatitis is an inflammation of the prostate gland , which may be acute or chronic . Diagnosis of the disease is difficult because the symptoms can be very different from patient to patient. Many of the symptoms such as pain or burning in urination and frequency of urination can be symptoms of some other diseases. All forms of prostatitis affect sperm and thus fertility , that is why the young man of reproductive age should be examined by a urologist .Four types of prostatitis have been described:
- Acute Bacterial Prostatitis
- Chronic bacterial prostatitis
- Chronic non- bacterial prostatitis
- Asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis
Acute Bacterial Prostatitis
Acute prostatitis is acute inflammation of the prostate caused by microbes (bacteria ) and presents typically with high fever and severe local and general symptoms. Affects more often younger men. The cause of acute prostatitis are germs (bacteria ) . The most common bacterium is Escherichia coli (E. Coli) and occasionally Pseudomonas.
Epididymitis
Epididymitis describes a clinical syndrome , which occurs with inflammation, pain and swelling of the epididymis . Acute epididymitis is inflammation of the epididymis, the organ which is above and behind the testicles into the scrotum and is part of the male reproductive system, where sperm is matured and stored. It is one of the urological emergencies, because it causes severe symptoms and also because in some cases clinical manifestation can imitate the torsion of testicle(!), therefore it requires a very careful examination to clarify which of these two pathologies we’re dealing with.Inflamation is of primarily microbial etiology. The most common pathogens are: E.coli, enterococci , klempsiella etc., and for nonspecific: chlamydia, ureaplasma, mycoplasma, mainly in young people. Sometimes where there are severe symptoms and high fever the patient may need hospitalization to receive intravenous antibiotics. Surgery is indicated in those cases only where an abscess has formed and requires draining.
The inflamation of epididymis can lead to temporary or even permanent infertility. Chronic epididymitis occurs after recurrent acute epididymitis and may cause scarring and hardening of the epididymis. If epididymitis is bilateral, it can cause infertility.
Cystitis
Cystitis is an infection of the bladder. It occurs when the urine is sterile under normal conditions , infected by germs entering almost always by the urethra . The more frequent responsible bacteria is Escherichia coli or E. Coli in 90% of cases. It is estimated that 40 % of women will experience at least one lifetime episode of acute cystitis. The usual symptoms of cystitis are:- Pain during urination
- Burning when urinating (stinging)
- Frequent urination
- Urgent urination
- Blood in the urine
- Cloudy and smelly urine
The diagnosis is made by the urologist with history taking and byclinical examination. The clinical examination of a patient with urinary tract infection should include the examination of the external and internal genitalia . The importance lies in the fact that gynecological problems such as vaginitis , may present with symptoms of UTI . Further radiological assessment is considered necessary only in cases of relapses of UTIand includes NOK radiography , ultrasound kidney – bladder.




